C++提供了一小部分runtime introspection的能力(RTTI: Run-Time Tyep Identification)
typeidstd::type_info- …
但是这些能力非常有限,不支持reflection ,且会带来运行时开销。所以本篇笔记重点介绍一下如何用在C++中实现compile-time introspection。
1 函数调用背后发生了什么
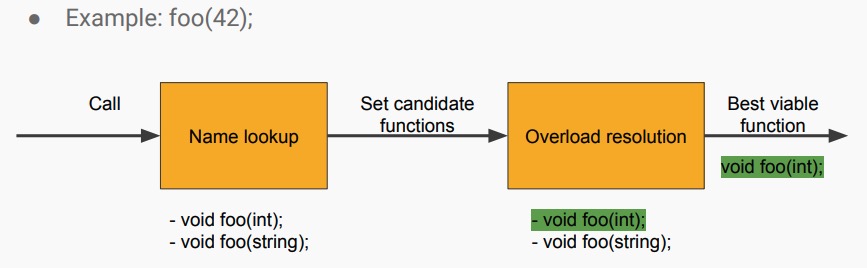
1.1 一般函数调用过程
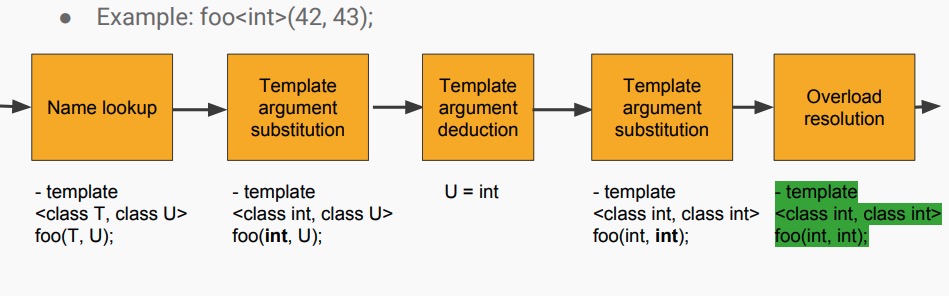
1.2 函数模板实例调用过程
1.3 SFINAE
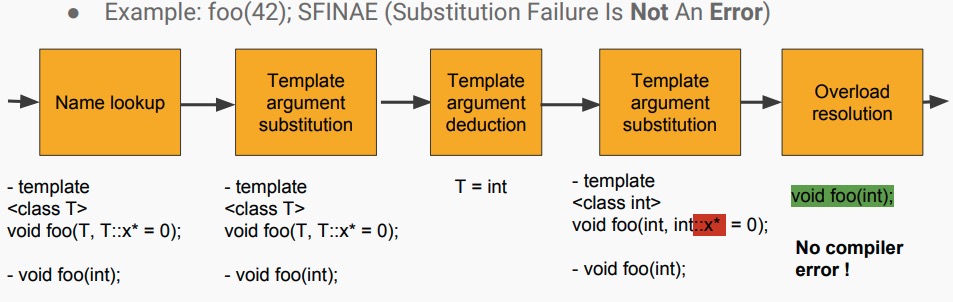
(Type) SFINAE(Substitution Failure Is Not An Error) let’s write potentially invalid template code without throwing an error;
Of course, if there is no alternative candidate, this will be an error!
- name lookup: 名字查找
- overload resolution:重载决议
1.4 重载决议的规则

1 | void foo(unsigned int i); // (1) |
42是int类型,如果匹配(1),需要做type conversion,所以这里会和(2)匹配上
1 | void foo(unsigned int i); // (1) |
和(2)匹配会出现substitution failure,这里和(1)匹配上.
SFINAE的一个主要应用场景:introspection 。C++并不擅长在运行时检查对象的类型或属性,在这方面C++提供的最佳能力就是RTTI.
2 编译时自省
2.1 C++98的实现方式
2.1.1 具体实现
- 根据重载决议的规则,如果存在函数模板和可变参函数,优先考虑函数模板
可变参函数(variadic function)的概念,详细描述见cppreference: variadic functions。举个例子,像C中的printf(const char* format...)就是一个典型的可变参函数。 SFINAEsizeof(X)在编译时就能够获得X的字节数讲解样例:这里以将对象进行序列化(serialize)为例。有的对象内部定义了1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27template <class T>
struct has_type_x {
// Discriminateive return types
typedef char yes[1];
typedef char no[2];
template <class C>
static yes& test(typename C::x* = 0);
// Sink if no member called x in C
template <class C>
static no& test(...);
enum { value = sizeof(test<T>(0)) == sizeof(yes) };
};
struct A {
typedef int x;
};
int main() {
A a;
std::cout << has_type_x<A>::value << std::endl; // 1
std::cout << has_type_x<int>::value << std::endl; // 0
char test[has_type_x<A>::value * 4 + 40];
return 0;
}serialize方法,那么可以调用该方法进行序列化;有的对象比如int、float等对象没有serialize方法,可以通过一个公共的函数将其序列化(为了简单和便于理解,这里假设这个共用的函数为to_string)。1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29template <class T>
struct has_serialize {
typedef char yes[1];
typedef char no[2];
// This helper struct permits us to check that serialize is truly a method.
// The second argument must be of the type of the first.
// For instance:
// really_has<int, 10> would be substituted by reallyHas<int, int 10> and works!
// really_has<int, &C::serialize> would be substituted by reallyHas<int, int &C::serialize> and fail!
// Note: It only works with integral constants and pointers (so function pointers work).
// In our case we check that &C::serialize has the same signature as the first argument!
// really_has<std::string (C::*)(), &C::serialize> should be substituted by
// really_has<std::string (C::*)(), std::string (C::*)() &C::serialize> and work!
template <typename U, U u> struct really_has;
// Two overloads for yes: one for the signature of a normal method, one is for the signature of a const method.
// std::string (C::*)() is function pointer declaration.
template <typename C> static yes& test(really_has<std::string (C::*)(), &C::serialize>*) { }
template <typename C> static yes& test(really_has<std::string (C::*)() const, &C::serialize>*) { }
// Fallback for types without serialize(), the famous C++ sink-hole.
// Note that sink-hole must be templated too as we are testing test<T>(0).
template <typename> static no& test(...) { /* dark matter */ }
// The constant used as a return value for the test.
// The test is actually done here, thanks to the sizeof compile-time evaluation.
static const bool value = sizeof(test<T>(0)) == sizeof(yes);
};
问题: 通过has_serialize这个类模板,我们可以判断某个类型T 是否有serialize 这个函数,那么如何借助has_serialize进行序列化呢?
回答:
不work的
serialize:
对于
int而言,虽然在运行时不会走第一个分支,但是编译器检查时,仍然会考虑第一个分支。这就要求obj必须有serialize方法以及对应的to_string重载。可以work的
serialize:
2.1.2 std::enable_if介绍
- 阅读cppreference:std::enable_if,
std::enable_if可能的实现方式为:

这样,std::enable_if<true, T>::type即为T,std::enable_if<false, T>::type会引发编译错误(在SFINAE下,将不包含这一enable_if的函数/类作为候选)
- 表达式
typename std::enable_if<true, T>::type、std:enable_if_t<true, T>、typename std::enable_if<false, T>::type、std::enable_if_t<false, T>的含义:

2.1 Modern C++实现方式
2.1.1 使用declval、decltype(利用Expression SFINAE)和constexpr实现
std::declval
cppreference对std::declval 的描述如下:Converts any type
Tto a reference type, making it possible to use member functions in the operand of the decltype specifier without the need to go through constructors.std::declvalis commonly used in templates where acceptable template parameters may have no constructor in common, but have the same member function whose return type is needed.
Note thatstd::declvalcan only be used in unevaluated contexts and is not required to be defined; it is an error to evaluate an expression that contains this function. Formally, the program is ill-formed if this function is odr-used.
比如下面这个例子, NonDefault这个struct里没有构造函数, 通过std::decval可以访问它的成员函数,通过decltype推断该函数返回值的数据类型。
1 | struct NonDefault { |
std::decltype
decltype可以进行类型推断,具体细节可以阅读cppreference以及《Modern Effective C++》。这里解释一下上面decltype(std::declval<NonDefault>().foo(), bool()) n3 = 1;这条语句。这里的decltype并不是有两个参数,应该把括号里的看成一个逗号分隔的表达式。
decltype does not take two arguments. Simply, it can can have an expression as its argument, and the comma operator is one way of creating expressions.
The C++ comma operator
,can create a chain of multiple expressions. In decltype, all the expressions will be evaluated, but only the last expression will be considered for the type.

2.1.2 使用std::true_type和std::false_type实现
std::true_typeandstd::false_type: types that encapsulate aconstexpr boolean“true” and aconstexpr boolean“false”1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19template<typename T, T v>
struct integral_constant {
static constexpr T value = v;
};
// 通过全特化,得到std::true_type和std::false_type
using true_type = integral_constant<bool, true>;
using false_type = integral_constant<bool, false>;
// 利用得到的std::true_type和std::false_type,可以检查某个类型是否为引用
template<typename T>
struct is_reference : false_type {};
// 这里对is_reference这个类模板进行了偏特化
template<typename T>
struct is_reference<T&> : true_type {};
template<typename T>
struct is_reference<T&&> : true_type {};关于type traits
- 大多数type traits都是self-explanatory的。比如
is_integral<T>、is_const<T>、is_member_function_pointer<T>等 - 也有少部分type traits会复杂一些。比如
conditional<B, T, F>、has_unique_object_representations<T>等 - 使用type traits,也可以选修改类型(在编译时)。比如
make_signed<T>、add_const<T>、add_pointer<T>等。
关于各种type taits,可以在cppconference中阅读相关词条。
- 大多数type traits都是self-explanatory的。比如
3 其它

tag dispatch: 基本思想就是创建“tags”(empty structs)来引导重载决议。比如可以使用std::true_type和std::false_type作为tags。比如博客《boost源码剖析之:泛型编程精灵type_traits(rev#2)》 中分派一节介绍的其实就是tag dispatch(标签分派)。
4 参考资料
1 《Type Traits, SFINAE and Compile-Time Reflection》
2 《Video: Compile time type introspection using SFINAE》
Comments